你现在所在位置:资讯首页 > 专题讲座
Nature:人的GLUT1葡萄糖运输载体的结构被揭示
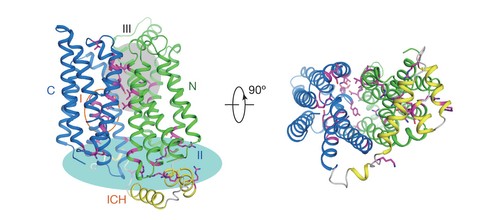
医学资讯 发布时间:2014-06-07 点击:GLUT1是负责葡萄糖向红血球和其他细胞中吸收的一种膜蛋白。一个质子耦合的木糖协同运输载体(它是GLUT1的一种细菌同源物)的结构以前曾被报道过,现在Nieng Yan及同事在这篇论文中报告了人GLUT1在一个向内开启的构形中的结构。获得这种人蛋白的结构后,作者便能够将与GLUT1缺陷综合征(亦称为De Vivo病)相关的失活性突变映射到它们的结构上。由于GLUT1的表达水平已被发现在几种癌症类型中升高,所以这一结构的获得也许会有助于新的潜在抗癌药物的开发。
原文链接:Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1
Abstract:The glucose transporter GLUT1 catalyses facilitative diffusion of glucose into erythrocytes and is responsible for glucose supply to the brain and other organs. Dysfunctional mutations may lead to GLUT1 deficiency syndrome, whereas overexpression of GLUT1 is a prognostic indicator for cancer. Despite decades of investigation, the structure of GLUT1 remains unknown. Here we report the crystal structure of human GLUT1 at 3.2 Å resolution. The full-length protein, which has a canonical major facilitator superfamily fold, is captured in an inward-open conformation. This structure allows accurate mapping and potential mechanistic interpretation of disease-associated mutations in GLUT1. Structure-based analysis of these mutations provides an insight into the alternating access mechanism of GLUT1 and other members of the sugar porter subfamily. Structural comparison of the uniporter GLUT1 with its bacterial homologue XylE, a proton-coupled xylose symporter, allows examination of the transport mechanisms of both passive facilitators and active transporters.
相关文章

高脂肪饮食或可延缓脑衰老一提到高脂肪饮食,人们第一之间往往想到的是肥胖,接下来就一...